
The information provided in this article is for general informational purposes only. While we endeavour to provide accurate and up-to-date information, there may be instances where information is outdated or incorrect. The contents of this article should not be taken as legal advice nor should it be relied upon in making any business, legal or other decisions. We encourage readers to consult with a qualified legal or professional advisor to obtain proper advice based on your unique circumstances. Cannavigia disclaims any liability for any loss or damage arising out of or in any manner connected with the use of or reliance on the information provided in this article.
Your one stop Thai shop (everything you always wanted to know about Thailand and cannabis but didn’t know who to ask)
Table of contents:
1. Cannabis Licensing History
2. Licensing Guide & Checklist
3. New GACP Guidelines in Thailand
4. GACP Requirements & Application
Want to do business in Thailand? Well, here is all the info you need, including licensing requirements, checklists and updated regulations around Good Agricultural and Collection Practices (GACP) inspections.
Cannabis Licensing History
Regulations & License Requirements
In the first part of the Thailand Country Report, we covered the history of cannabis in Thailand and the evolution of the regulatory landscape until the removal of cannabis from the Category 5 Narcotics list on June 9th, 2022. In this part, we’ll cover what the regulations are in place at the moment, as well as provide a guide to cultivating cannabis in Thailand.
Since the surprise announcement in June 2022, Thais have taken full advantage of this legal grey area while awaiting the long-anticipated Cannabis Bill. As you read this, on Bangkok’s Khao San Road street side tables are groaning under the weight of piles of buds.
Thailand’s tropical climate is ideal for growing cannabis, and the government wants to make a splash in the market for medical cannabis. It is projected to boost everything from national income to small farmers’ livelihoods. “We should know how to use cannabis,” Public Health Minister Anutin Charnvirakul, the country’s biggest cannabis supporter, said. “If we have the right awareness, cannabis is like gold, something valuable, and should be promoted.”
With this vision in mind, let’s explore what regulations are governing this bustling industry in Thailand:
Removal of Cannabis and Hemp Plants from the Category 5 Narcotics List on 9th June, 2022
On 9th June, 2022, 120 days after its publication in the Royal Gazette, the Thai Food and Drug Administration officially removed cannabis and hemp plants from the Category 5 narcotics list. Thailand’s health minister Anutin Charnvirakul started to distribute free cannabis plants to households across the country. The move is said to be a step further into Thailand’s plan to use cannabis as a cash crop. Around 4,200 prisoners were released as a result of the decriminalisation on the same day.
Nevertheless, extractions from the cannabis plant are still categorized as Category 5 Narcotics, along with poppy plants (Papaver somniferum L.) and psilocybin. The exemptions to this are:
- Cannabis extractions with THC less than 0.2% by weight, that have been granted permission to be extracted from cannabis/hemp plants grown in Thailand
- Cannabis/hemp seed oil from cannabis/hemp plants grown in Thailand
Regulations Governing Cannabis/Hemp use in public areas
While recreational cannabis has been actively frowned upon by the Ministry of Public Health, there were no immediate laws in place to prevent recreational cannabis smoking.
In the Public Nuisance Announcement B.E. 2565 (2022) on 14th June, the MOPH specified that the act of creating cannabis or hemp smoke in public is considered a public nuisance and can be charged accordingly. The Department of Health said that the regulation is aimed at preventing recreational use of cannabis/hemp and the causing of nuisance and health hazards to others.
In another announcement by the MOPH on 16th June 2022, Cannabis and hemp effectively became classified as a Controlled Herb with the following rules:
- Those over the age of 20 are able to possess, cultivate, distribute and sell controlled herbs with the exception of the following activities:
- Smoking in public spaces
- Consumption by pregnant or breastfeeding women
- Selling to pregnant or breastfeeding women
While these laws aim to curb the recreational use of cannabis products, there are still many loopholes, and a bustling grey market. Nevertheless, certain licenses are required for certain activities, such as selling of cannabis products. Import and export of cannabis are still highly regulated.
Sources
https://cannabis.fda.moph.go.th/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/law_NYS5_080265.pdf
https://www.lonelyplanet.com/news/khao-san-road-cleans-up
https://cannabis.fda.moph.go.th/wp-content/uploads/2022/06/Law_T0002_150665.pdf
https://mnfda.fda.moph.go.th/narcotic/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/PK65_herbs_160765.pdf
Licensing Guide & Checklist
How to get your license in Thailand
The legal entity must be registered in accordance with Thai law. At least two-thirds of the directors, partners, or shareholders must have Thai nationality and have an office in Thailand.
A license for the cultivation
- Cannabis cultivation can be carried out without permission, but only by notice/register.
- Growers must register on the mobile app or website “Plookganja”. The following questions will be asked:
- Register your account at https://plookganja.fda.moph.go.th/
- ID number
- Phone number
- Purpose of cultivation
- Use household benefits for health care.
- Taking care of patients in traditional Thai medicine.
- For commercial and industrial use
- Use in research
- What is your cultivation?
- Cannabis
- Hemp
- How many plants?
- Source
- Original licensee/government agency
- Import
- 1 million cannabis cultivation projects (Receive cannabis seedlings from the Department of Agriculture)
- Other items used for planting:
- Seeds
- Cuttings
- Seedlings
- Tissue culture
- Address of your cultivation site
- Planting location details – describe in text:
- Latitude and longitude
- Legal entity operator number (e.g. Legal entity number, tax identification number Community enterprise registration number)
- Operator name
- What is it grown for? – describe in text:
- Area (square meters)
- Register your account at https://plookganja.fda.moph.go.th/
![Download Now: Free Cannabis Licensing Guide for Thailand [Get Your Guide]](https://no-cache.hubspot.com/cta/default/6213174/41ce9020-3a79-4ec6-8754-f242855bb35e.png)
Get in touch to find out more about the current situation in Thailand and how we can support your cultivation.
New GACP Guidelines in Thailand
Please be aware that the information presented from here reflects the updated GACP guidelines established by the Thai government in September 2023.
When Thailand took cannabis off the prohibition list in February 2021, there were a lot of things left hanging in the air. From this chaos emerged a working system that allowed a lot of freedom, but things are changing fast. The new premier (as of September 2023) Srettha Thavisin, told Bloomberg TV in an interview that his government would seek to “rectify” the law on cannabis within the next six months, suggesting that the plant would remain legal only for medical use. This may come at a huge loss of income for those benefitting from the loose legal framework within which they are operating.
In line with the government’s plans to regulate medical cannabis, they have published a set of laws that determine their GACP as well as a complete list to qualify for a license. They have also published a list of requirements for the certification of the GACP.
GACP Requirements & Application
Requirements for certification of good cultivation and collection practices for cannabis plants in Thailand:
Entrepreneurs must comply with the requirements for certification of Thailand GACP. There are basic requirements that every entrepreneur must comply with
1. Entrepreneurs must keep records continuously. Because the inspector may need to check all these documents:
- Record the purchase and use of production factors in the planting plots
- Record of activities
- Record the sale of produce or other documents related.
2. Entrepreneurs must keep documents and continuous records, such as:
- Raw material certificates and raw material order documents
- Raw material receipt
- Raw material – stock processing/packaging
- Records stock – products sales documents/delivery notes,
- Cleaning records – record the prevention and elimination of insects/pests in the planting plot.
- Compliant records and other related documents – allow the inspector to check whether it is according to the standards or not
3. Allow staff to inspect documents related to planting and preliminary processing:
- Allow staff to inspect all owned planting areas (self-operated, leased), including:
- Certified and non-certified facilities as well as equipment storage facilities and storage facilities
- Product, raw material storage facilities and accommodation do not require prior notice.
4. If there are changes that do not meet the specified standards such as varieties, planting locations and additional certification requests, the operator must immediately notify the department.
5. In case the operator hires others for production or management, the operator must sign a subcontracting contract with the contractor.
6. Entrepreneurs must keep the following documents for department inspection for no less than 5 years.
- Copy of Application Form
- Copy of Department Official Inspection Report
- Certification Results
- Compliant records (if any)
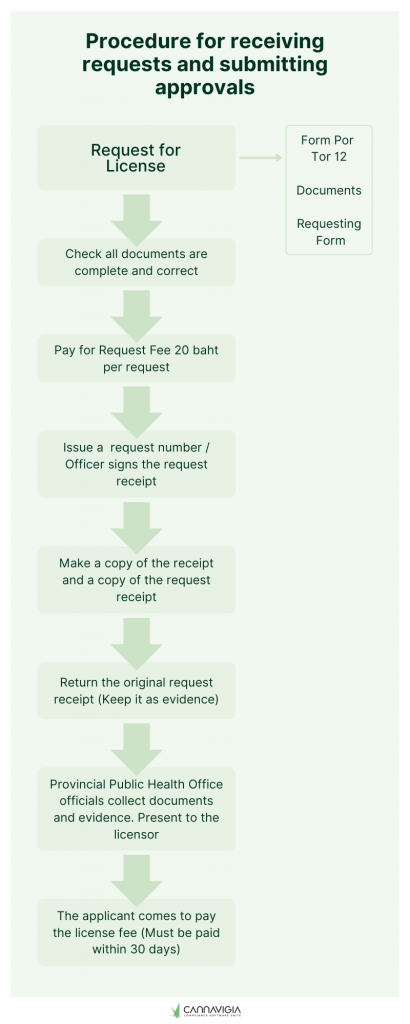
Once you have stuck to these rules, you have to apply for your GACP certification. The process works as follows:
Ok, now that you know how the bureaucratic aspect works, it’s time to get down to the nitty gritty of what exactly is expected of you with regards to your crop. These are the GACP requirements translated to English.

Comments